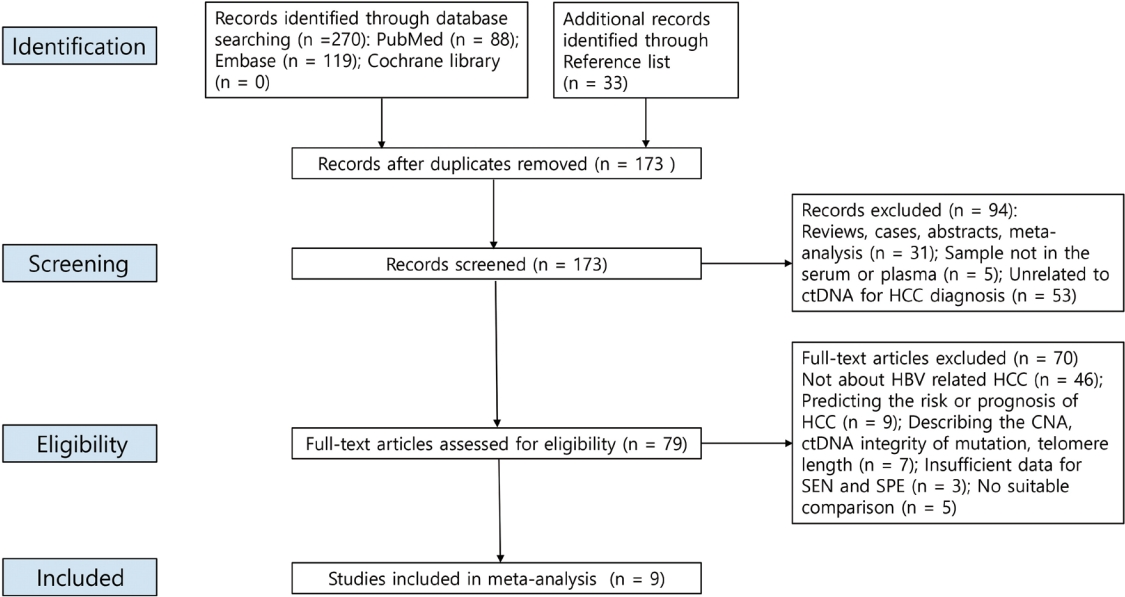
- The diagnostic value of circulating tumor DNA in hepatitis B virus induced hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
Young Chang, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, Hyuksoo Eun, Young‑Sun Lee, Do Seon Song, Su Jong Yu, Sae Hwan Lee, Won Kim, Hyun Woong Lee, Sang Gyune Kim, Seongho Ryu, Suyeon Park
-
J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):167-177. Published online September 29, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.09.19
-
-
2,603
Views
-
73
Downloads
-
1
Citation
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material
- Background/Aim
New biomarkers are urgently needed to aid in the diagnosis of early stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We performed a meta-analysis on the diagnostic utility of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) levels in patients with hepatitis B virus-induced HCC.
Methods
We retrieved relevant articles from PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library up to February 8, 2022. Two subgroups were defined; one subset of studies analyzed the ctDNA methylation status, and the other subset combined tumor markers and ctDNA assays. Pooled sensitivity (SEN), specificity (SPE), positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and area under the summary receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) were analyzed.
Results
Nine articles including 2,161 participants were included. The overall SEN and SPE were 0.705 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.629-0.771) and 0.833 (95% CI, 0.769-0.882), respectively. The DOR, PLR, and NLR were 11.759 (95% CI, 7.982-17.322), 4.285 (95% CI, 3.098- 5.925), and 0.336 (0.301-0.366), respectively. The ctDNA assay subset exhibited an AUC of 0.835. The AUC of the combined tumor marker and ctDNA assay was 0.848, with an SEN of 0.761 (95% CI, 0.659-0.839) and an SPE of 0.828 (95% CI, 0.692-0.911).
Conclusions
Circulating tumor DNA has promising diagnostic potential for HCC. It can serve as an auxiliary tool for HCC screening and detection, especially when combined with tumor markers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - 16S rRNA Next-Generation Sequencing May Not Be Useful for Examining Suspected Cases of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
Chan Jin Yang, Ju Sun Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Keun Woo Park, Jina Yun, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(2): 289. CrossRef
- Recent Advances and Future Directions in Immunotherapeutics for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
Yuri Cho, Jimin Han, Won Kim
-
J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(1):1-11. Published online March 31, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.1.1
-
-
5,105
Views
-
144
Downloads
-
5
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Systemic target therapeutic drugs, such as sorafenib, lenvatinib, or regorafenib are the only drugs that are known to be effective against advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, these agents show a limited efficacy in killing residual tumors. Immunotherapy is an alternative approach to this treatment and has been used to successfully treat different cancers, including HCC. HCC is an inflammation-induced cancer and represents a very interesting target for immunotherapeutics. Immunotherapies aim to reverse the immune tolerance and suppression found in tumor microenvironments and include approaches, such as adoptive cell therapy, immune checkpoint inhibition, and cancer vaccination. Adoptive cell therapy uses autologous natural killer or cytokine-induced killer cells by cultivating them ex vivo and subsequently reinfusing them into the patient. Immune checkpoint inhibitors reactivate tumorspecific T cells by suppressing checkpoint-mediated inhibitory signaling. Cancer vaccination induces a tumor-specific immune response by activating effector T lymphocytes. A wide range of potential immunotherapy-related adverse events occur; therefore, a multidisciplinary collaborative management is required across the clinical spectrum. This review summarizes the current status of immunotherapy for HCC and provides a perspective on its future applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Exploring the potential of Toxoplasma gondii in drug development and as a delivery system
Chanjin Yoon, Yu Seong Ham, Woo Jin Gil, Chul-Su Yang
Experimental & Molecular Medicine.2024; 56(2): 289. CrossRef - Comparison of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis
Jeayeon Park, Yun Bin Lee, Yunmi Ko, Youngsu Park, Hyunjae Shin, Moon Haeng Hur, Min Kyung Park, Dae-Won Lee, Eun Ju Cho, Kyung-Hun Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Su Jong Yu, Tae-Yong Kim, Yoon Jun Kim, Tae-You Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 81. CrossRef - Revamping the innate or innate-like immune cell-based therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: new mechanistic insights and advanced opportunities
Disha D. Shah, Bhavarth P. Dave, Parv A. Patel, Mehul R. Chorawala, Vishvas N. Patel, Palak A. Shah, Manish P. Patel
Medical Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Differences between exhausted CD8+ T cells in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with and without uremia
Chen Xiaohong, Zou Jianzhou, Shen Bo, Lv Wenlv, Cao Xuesen, Xiang Fangfang
Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology.2021; 99(4): 395. CrossRef - Nivolumab for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Multiple Lung Metastases after Sorafenib Failure
Jaewoong Kim, Jin Won Chang, Jun Yong Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2020; 20(1): 72. CrossRef
- Prediction of Tumor Biology in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
Won Kim
-
Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2009;9(1):1-6. Published online June 30, 2009
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) surveillance programs have led to an increase in the adoption of radical therapies.
Nevertheless, HCCs often present at an advanced stage and the prognosis remains dismal even after resection due to the high rate
of recurrence. The study of tumor biology is important to predict clinical outcome enabling more appropriate therapeutic decisions
for HCC patients. Understanding molecular mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis may also lead to effective strategies in
chemoprevention. However, current staging systems based on clinicopathologic factors are limited in prognostic prediction.
Recently, there has been great interest in the study of gene expression profile in relation to prognosis of HCC. Global gene
expression profiling may be the most appropriate technology to unravel the pathogenesis of HCC and explore its heterogeneous
origin. The elucidation of tumor biology of HCC is of paramount clinical importance in the new era of molecular target therapy.
|